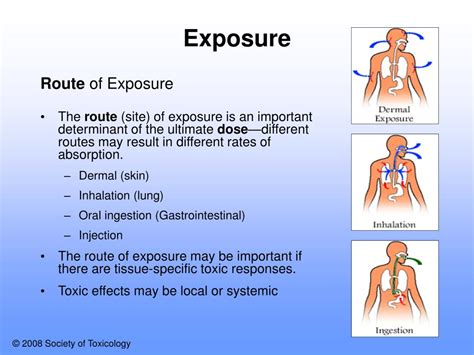
Types of Poisoning: Understanding the Different Routes of Exposure
Ingestion: The Most Common Route of Poisoning
The act of ingestion refers to the process of taking substances into the body through the mouth. It is a common route of poisoning and is responsible for a significant number of poisoning cases around the world. Ingested toxic substances can range from household chemicals, medications, contaminated food and water, to even plants and mushrooms. This blog post aims to shed light on the dangers associated with ingestion and the steps that can be taken to prevent accidental poisoning through this route.
The Dangers of Ingested Toxins
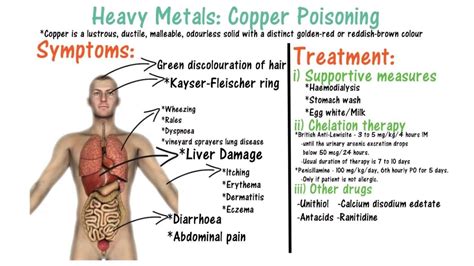
When toxic substances are ingested, they can have detrimental effects on the body. The severity of the poisoning can vary depending on the type of toxin, the quantity ingested, and the individual’s overall health. Common symptoms of ingestion poisoning may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and in more severe cases, organ damage or failure.
Children are particularly vulnerable to ingestion poisoning as they are curious by nature and tend to explore their surroundings by putting objects into their mouths. It is crucial for parents and caregivers to be aware of potential hazards within their homes and ensure that toxic substances are stored out of reach and in child-proof containers.
Preventing Ingestion Poisoning
Prevention is the key to reducing the incidence of ingestion poisoning. Here are some measures that can be taken:
- Keep toxic substances out of reach: Store chemicals, cleaning products, medications, and other potentially toxic substances in high cabinets or locked containers.
- Properly label containers: Ensure that all containers are clearly labeled to avoid any confusion or accidental ingestion.
- Child-proof your home: Use safety latches on cabinets, install child-proof locks on drawers, and secure appliances and furniture to prevent children from accessing potentially harmful substances.
- Dispose of medications properly: Safely discard expired or unused medications by following the guidelines provided on the packaging or seeking guidance from a pharmacist.
- Be cautious with food and drinks: Avoid consumption of expired or contaminated food and drinks. Regularly check the condition of canned goods and be aware of any potential food recalls.
What to Do in Case of Ingestion Poisoning?
If ingestion poisoning is suspected, it is crucial to take immediate action:
- Call emergency services: Dial the emergency services number in your country immediately to seek professional help.
- Do not induce vomiting: Unless instructed to do so by a medical professional, refrain from inducing vomiting as it may further harm the individual.
- Provide relevant information: Provide the emergency responders with any information regarding the ingested substance, quantity, and symptoms observed.
- Follow medical advice: Cooperate with medical professionals and follow their instructions for the best possible outcome.
Conclusion
Ingestion is the most common route of poisoning, posing a significant risk to individuals, particularly children. It is essential to be proactive in preventing ingestion poisoning by practicing proper storage of toxic substances, child-proofing your home, and maintaining caution with food and drinks. In case of ingestion poisoning, quick action is necessary, including contacting emergency services and providing relevant information for prompt and appropriate medical intervention. By raising awareness about the dangers of ingestion and adopting preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the incidences of poisoning through this route.
Inhalation: Understanding the Dangers of Airborne Toxins
Inhalation is one of the most common routes through which individuals can be exposed to toxic substances. Airborne toxins can be present in various environments, including workplaces, homes, and outdoor areas. Understanding the dangers associated with inhaling these toxins is crucial for both personal and public health.
When we breathe in, our lungs act as the main entry point for air and everything it contains, including pollutants and hazardous chemicals. Airborne toxins can come in the form of gases, vapors, fumes, or particulate matter. These toxins can be released from various sources such as industrial processes, vehicle emissions, cigarette smoke, or even natural events like wildfires.
Exposure to airborne toxins can have severe health effects, ranging from short-term irritation to long-term chronic conditions. The type and severity of these effects depend on several factors, including the nature of the toxic substance, concentration, duration of exposure, and the individual’s overall health.
Some common health issues associated with inhalation of airborne toxins include respiratory problems, such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Additionally, exposure to certain airborne toxins has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders.
It is important to understand that everyone is potentially at risk of inhaling airborne toxins, but certain individuals may be more vulnerable. For instance, children, elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions may experience more severe health effects due to inhalation exposure.
To protect ourselves from the dangers of airborne toxins, it is essential to take preventive measures. Some effective strategies include ensuring proper ventilation in indoor spaces, using personal protective equipment (such as masks) when necessary, and minimizing exposure to known pollutants. Additionally, adopting sustainable practices and supporting policies aimed at reducing overall air pollution can benefit not only our individual health but also the health of the planet.
Overall, the understanding of the dangers associated with inhaling airborne toxins is vital for promoting a healthier environment and safeguarding our well-being. By being aware of the potential risks and taking necessary precautions, we can strive towards minimizing exposure and creating safer living and working environments for ourselves and future generations.
Dermal Contact: How Toxic Substances Can Enter through the Skin
When it comes to understanding the various routes of poisoning, dermal contact is a crucial aspect to consider. Our skin is more than just a protective barrier; it can also serve as an entry point for toxic substances to enter our bodies. In fact, dermal exposure is one of the most common ways for harmful chemicals, gases, and other toxins to infiltrate our systems. In this blog post, we explore the dangers of dermal contact and shed light on how toxic substances can easily find their way through our skin.
1. The Skin: More Than Meets the Eye
Our skin, the largest organ in the human body, is composed of multiple layers including the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. While it primarily acts as a barrier against external threats, such as bacteria and UV radiation, it is not entirely impermeable. The outermost layer of the skin, the epidermis, is responsible for the protective function. However, it is not resistant to all substances, especially those that are chemically active or can penetrate through the skin’s pores.
2. Common Toxic Substances that Enter through the Skin
There is a wide range of toxic substances that can enter our bodies through dermal contact. These substances vary in their nature and include chemicals found in cleaning products, pesticides, solvents, heavy metals, and even certain medications. Additionally, some industrial chemicals and occupational hazards pose a significant risk when they come into contact with the skin. It is important to be aware of these substances and take necessary precautions to minimize exposure.
3. The Dangers of Dermal Exposure
Dermal exposure to toxic substances can lead to various health issues, ranging from mild irritations to severe systemic effects. Immediate symptoms may include redness, itching, and even burning sensations. Prolonged or repeated exposure to certain substances can result in chronic skin conditions, such as dermatitis or chemical burns. Furthermore, toxic substances that penetrate the skin can enter the bloodstream and potentially affect internal organs, leading to more serious health complications.
4. Prevention and Protection
Minimizing dermal contact with toxic substances is essential to safeguarding our health and well-being. Here are some preventive measures one can take:
- Wearing protective clothing, such as gloves and long-sleeve shirts, when handling chemicals or potentially hazardous materials.
- Using personal protective equipment, including goggles and face masks, to shield the eyes and respiratory system from airborne toxins.
- Practicing good hygiene by promptly washing hands and exposed skin after potential contact with toxic substances.
- Awareness and education regarding the risks associated with specific substances, especially in occupational settings.
Conclusion
Understanding the risks associated with dermal contact is crucial for maintaining our overall health and well-being. By being aware of the various toxic substances that can enter through the skin and taking preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the potential harm they may cause. Remember, our skin may seem tough, but it is not invincible when it comes to toxic invaders.
Injection: Recognizing the Risks of Injected Poisons
Injection is a common route of administering medication or vaccines to the body. However, it can also be a dangerous method when it comes to the potential risks of injected poisons. Understanding these risks is crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals receiving injections.
Firstly, it is important to recognize that injected poisons can enter the bloodstream directly, bypassing the body’s natural defense mechanisms. This means that the effects of these substances can be more potent and immediate compared to other routes of exposure. The rapid absorption of injected poisons can lead to severe health complications or even fatal consequences, especially if proper precautions are not taken.
Secondly, the risk of infection is another significant concern when it comes to injected poisons. If the injection equipment is not properly sterilized or if the injection site is contaminated, harmful bacteria or viruses can be introduced to the body. This can result in localized infections, such as abscesses or cellulitis, or even systemic infections that can spread throughout the body. Therefore, maintaining strict hygiene protocols and using sterile equipment is imperative to minimize the risk of infections.
Lastly, it is essential to recognize the potential for allergic reactions or adverse effects when injecting poisons. Different individuals may have varying sensitivities or allergies to certain substances, and injecting these poisons can trigger severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to be aware of these risks and monitor patients closely during and after the injection to promptly address any adverse reactions that may occur.
In summary, recognizing the risks associated with injected poisons is vital in order to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals receiving injections. By understanding the direct and immediate impact on the body, the potential for infections, and the possibility of allergic reactions, healthcare professionals can take appropriate measures to mitigate these risks. Implementing proper sterilization practices, maintaining hygiene protocols, and closely monitoring patients are all crucial steps in minimizing the risks associated with injected poisons.
Absorption: Uncovering the Silent Danger of Absorbed Toxins
When we talk about toxic substances entering our bodies, we often think about the more obvious routes such as ingestion or inhalation. However, there is another way that toxins can silently infiltrate our system – through absorption. Absorption refers to the process by which substances are taken in and penetrate our skin, mucous membranes, and other tissues. While we may not always be aware of it, absorption can pose a significant risk to our health.
One common example of absorption is the use of skincare products. Many of us are in the habit of using creams, lotions, and other beauty products on a daily basis. However, what we may not realize is that some of these products contain harmful chemicals that can be absorbed through our skin. Ingredients like parabens and phthalates have been linked to various health issues, including hormone disruption and even cancer.
Another source of absorbed toxins is our environment. We are constantly surrounded by chemicals and pollutants, from the air we breathe to the water we swim in. Prolonged exposure to these toxins can lead to their absorption through our skin or even through the pores of our scalp. It’s important to be mindful of our surroundings and take steps to minimize our exposure to harmful substances.
So, what can we do to protect ourselves from the silent danger of absorbed toxins? Firstly, it’s crucial to be aware of the ingredients in the products we use. Reading labels and opting for natural, organic alternatives can significantly reduce our risk of absorption. Additionally, we should be mindful of our surroundings and try to minimize exposure to toxins whenever possible. This may include using protective gear when working with hazardous substances or opting for organic and chemical-free cleaning products.
To summarize:
| Absorption | – | The process by which substances are taken in and penetrate our skin, mucous membranes, and other tissues. |
| Sources | – | Skincare products, environmental pollutants |
| Risks | – | Hormone disruption, cancer, and other health issues |
| Protection | – | Read labels, choose natural products, minimize exposure to toxins |
While absorption may not be as widely recognized as other routes of toxin entry, it is essential to understand and address the risks it poses. By being educated and proactive, we can minimize our exposure to absorbed toxins and protect our long-term health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: How can poisoning occur through ingestion?
Poisoning through ingestion occurs when toxic substances are accidentally or intentionally consumed. This can happen by ingesting contaminated food or drinks, taking medication in incorrect doses, or swallowing harmful substances, among others.
Question 2: What are the dangers of airborne toxins in inhalation?
Inhalation of airborne toxins can lead to various health risks. Breathing in toxic gases, fumes, or particles can cause respiratory problems, irritation, lung damage, and even systemic effects if the toxins enter the bloodstream.
Question 3: How do toxic substances enter the body through dermal contact?
Toxic substances can enter the body through the skin via dermal contact. This can occur when individuals handle or come in direct contact with poisonous substances, leading to absorption through the skin layers and potential health hazards or systemic effects.
Question 4: What are the risks associated with injected poisons?
Injected poisons pose serious risks as they introduce toxic substances directly into the bloodstream. Whether it is through drug injections or venomous bites, injected poisons can cause immediate and severe reactions, organ damage, and in some cases, be life-threatening.
Question 5: What is the silent danger of absorbed toxins?
Absorbed toxins present a silent danger as they can enter the body through various means such as inhaling, ingesting, or dermal contact. These toxins can accumulate over time, affecting organs, disrupting bodily functions, and potentially causing chronic illnesses or long-term health issues.
Question 6: How can one prevent poisoning through ingestion?
To prevent poisoning through ingestion, it is essential to practice proper food safety measures, store and handle chemicals or medications safely, keep harmful substances out of reach of children, and educate oneself about potential hazards and proper usage.
Question 7: What precautions should be taken to avoid skin absorption of toxic substances?
To minimize the risk of skin absorption of toxic substances, it is crucial to wear appropriate protective clothing and gear, such as gloves or masks, when handling chemicals or known hazardous materials. Thoroughly washing the skin after contact and avoiding prolonged exposure to harmful substances are also essential precautionary measures.