Organophosphate Poisoning
What is Organophosphate Poisoning?
Organophosphate poisoning refers to the toxic effects caused by exposure to organophosphate compounds. Organophosphates are a class of chemicals that are commonly used as pesticides and insecticides in agriculture and domestic settings. These compounds work by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase, which is responsible for breaking down a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. When acetylcholinesterase is inhibited, the levels of acetylcholine increase, leading to excessive stimulation of the nervous system.
Organophosphate poisoning can occur through various routes, including inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact with contaminated substances. It is important to note that these compounds can be highly toxic and even small amounts can cause significant harm. Common sources of exposure include agricultural spraying, improper handling of pesticides, and accidental ingestion of household chemicals.
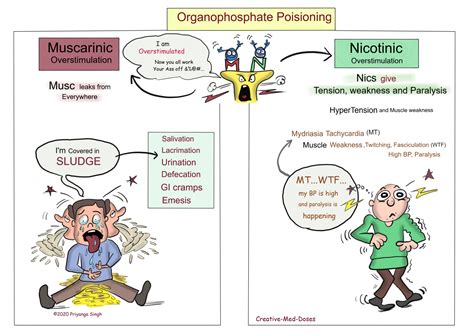
The signs and symptoms of organophosphate poisoning can vary depending on the degree of exposure and individual susceptibility. The initial symptoms may include increased salivation, sweating, blurred vision, and muscle twitching. As the poisoning progresses, individuals may experience difficulty breathing, chest tightness, tremors, and even seizures. In severe cases, organophosphate poisoning can lead to respiratory failure, coma, and death.
Seeking immediate medical attention is crucial if organophosphate poisoning is suspected. The treatment options for organophosphate poisoning primarily focus on decontamination and counteracting the effects of the toxic compound. The affected individual may undergo decontamination procedures, such as washing the skin or eyes with water, and removing contaminated clothing. Medical professionals may administer medications, such as atropine and pralidoxime, to counteract the effects of acetylcholine and restore normal nerve function.
Preventing organophosphate poisoning is key to promoting safety and well-being. It is important to carefully follow the instructions on pesticide labels and use protective equipment when handling these chemicals. Proper storage and disposal of pesticides are also essential to prevent accidental exposure. Educating individuals in high-risk occupations and raising awareness about the potential dangers of organophosphates can contribute to reducing the incidence of poisoning cases.
Causes of Organophosphate Poisoning
Organophosphate poisoning refers to the toxic effects caused by exposure to organophosphate compounds, which are commonly used in pesticides and nerve agents. It is important to understand the various causes of organophosphate poisoning in order to prevent and effectively manage this potentially life-threatening condition.
1. Occupational Exposure: One of the primary causes of organophosphate poisoning is occupational exposure. Workers involved in industries such as agriculture, pest control, and chemical manufacturing are at a higher risk of coming into contact with these toxic compounds. Lack of proper protective measures, such as wearing gloves and masks, can further increase the risk.
2. Accidental Ingestion: Accidental ingestion of products containing organophosphates can occur, especially in children. Common sources of accidental poisoning include household pesticides, garden chemicals, and certain medications. It is crucial to store these substances safely out of the reach of children and follow the recommended guidelines for their use.
3. Intentional Poisoning: Unfortunately, organophosphate compounds are also used for self-harm or as a method of suicide. The ready availability of such compounds, combined with their potency, makes them a popular choice for individuals attempting intentional poisoning. Prompt intervention and access to mental health support are vital in preventing severe outcomes.
List of Common Causes of Organophosphate Poisoning:
- Occupational exposure
- Accidental ingestion
- Intentional poisoning
Table: Comparing Different Causes of Organophosphate Poisoning
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Occupational exposure | Occurs due to unprotected contact with organophosphate compounds at workplaces |
| Accidental ingestion | Ingestion of products containing organophosphates, commonly seen in children |
| Intentional poisoning | Deliberate ingestion of organophosphates for self-harm or suicidal purposes |
Being aware of the causes of organophosphate poisoning is crucial in order to minimize the risks associated with exposure to these toxic compounds. By implementing preventive measures, such as using protective equipment, storing chemicals safely, and promoting mental health support, we can work towards reducing the incidence of organophosphate poisoning and safeguarding the health and well-being of individuals.
Signs and Symptoms of Organophosphate Poisoning
Organophosphate poisoning is a serious condition that occurs due to the exposure or ingestion of chemicals called organophosphates. These chemicals are commonly used in pesticides, insecticides, and nerve agents. Although organophosphate poisoning is relatively rare, it can have severe consequences on human health. Being aware of the signs and symptoms of organophosphate poisoning is crucial in order to identify the condition and seek appropriate medical treatment promptly.
The signs and symptoms of organophosphate poisoning can vary depending on the level of exposure and individual susceptibility. However, there are some common indicators that can help recognize the condition. One of the initial symptoms is excessive sweating, which occurs due to the overstimulation of sweat glands by the chemicals. Additionally, individuals may experience pinpoint pupils, blurred vision, and excessive tears. These eye-related symptoms are a result of the toxic effect of organophosphates on the nervous system.
In more severe cases of organophosphate poisoning, individuals may exhibit symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and wheezing. This is due to the constriction and spasm of the airway muscles caused by the toxic chemicals. Furthermore, muscle weakness and twitching can occur as the organophosphates interfere with the proper functioning of the nerves and muscles. Abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are also common symptoms, as organophosphates can affect the gastrointestinal system.
It is important to note that organophosphate poisoning can have both immediate and delayed effects. Immediate effects appear shortly after exposure, whereas delayed effects can develop hours or even days later. Delayed symptoms may include anxiety, confusion, dizziness, and headache. In severe cases, seizures and loss of consciousness can occur.
- Excessive sweating
- Pinpoint pupils
- Blurred vision and excessive tears
- Difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and wheezing
- Muscle weakness and twitching
- Abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Anxiety, confusion, dizziness, and headache
- Seizures and loss of consciousness (in severe cases)
| Immediate Effects | Delayed Effects |
|---|---|
| Excessive sweating | Anxiety |
| Pinpoint pupils | Confusion |
| Blurred vision and excessive tears | Dizziness |
| Difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and wheezing | Headache |
| Muscle weakness and twitching | Seizures |
| Abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea | Loss of consciousness (in severe cases) |
If you suspect someone may be experiencing organophosphate poisoning, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly increase the chances of a successful recovery. Remember, early recognition of the signs and symptoms is vital in managing this potentially life-threatening condition.
Treatment Options for Organophosphate Poisoning
Organophosphate poisoning is a serious medical condition that occurs when a person is exposed to toxic chemicals known as organophosphates. These chemicals are commonly found in certain pesticides, insecticides, and even some medications. Treatment for organophosphate poisoning is crucial and should be initiated as soon as possible to minimize the potential long-term effects of exposure. In this blog post, we will explore the various treatment options available to manage organophosphate poisoning.
When it comes to treating organophosphate poisoning, medical professionals focus on three main approaches: decontamination, supportive care, and specific antidotes. Let’s take a closer look at each of these treatment options:
- Decontamination: The first step in treating organophosphate poisoning is to remove any contaminated clothing and thoroughly wash the affected individual to eliminate any remaining toxins on their skin. This helps reduce further absorption of the chemicals. Additionally, it may be necessary to decontaminate the area where the exposure occurred to prevent others from being exposed.
- Supportive care: Organophosphate poisoning can cause a range of symptoms, including difficulty breathing, increased heart rate, and muscle weakness. Supportive care aims to manage these symptoms and includes measures such as ensuring proper oxygenation and ventilation, maintaining fluid balance, and providing medications to stabilize heart rate and blood pressure.
- Specific antidotes: Antidotes are used to counteract the effects of organophosphates and restore normal bodily functions. One common antidote is atropine, which helps relieve symptoms associated with overstimulation of the nervous system. Another antidote, called pralidoxime, can be administered to reactivate the cholinesterase enzyme in the body, which is essential for normal nerve function.
In severe cases of organophosphate poisoning, additional interventions such as intubation to support breathing, seizure management, and hemodialysis may be necessary. It is important to note that treatment should always be managed by healthcare professionals in a controlled medical setting to ensure the safety and well-being of the individual.
Prevention remains the best approach to avoid organophosphate poisoning, and it is essential to follow safety guidelines when working with these chemicals. However, in the event of exposure, recognizing the signs and seeking immediate medical treatment can make a significant difference in the outcome.
In conclusion, treatment options for organophosphate poisoning involve decontamination, supportive care, and the administration of specific antidotes. Prompt and appropriate medical intervention is crucial to mitigate the effects of exposure. By understanding these treatment options, we can better protect ourselves and those around us from the harmful effects of organophosphates.
Preventing Organophosphate Poisoning
Organophosphate poisoning is a serious medical condition caused by the exposure to certain chemicals commonly found in pesticides, insecticides, and nerve agents. The effects can range from mild symptoms like headaches and dizziness to severe complications such as respiratory distress and paralysis. While treatment options are available, it is crucial to prioritize prevention to avoid the potentially life-threatening consequences of organophosphate poisoning.
1. Understand the potential hazards: Educating yourself and the community about the risks and dangers associated with organophosphates is the first step towards prevention. Knowledge about the sources of exposure and the symptoms of poisoning can help individuals take necessary precautions and seek timely medical assistance.
2. Handle pesticides with caution: If you use pesticides or insecticides in your home or garden, it is essential to follow the instructions carefully. Wear protective clothing, including gloves and masks, to minimize direct contact with the chemicals. After use, store these products in a secure location, away from children and pets.
3. Choose alternative methods: Whenever possible, explore and adopt natural or organic pest control methods. There are numerous eco-friendly alternatives available in the market that reduce the dependency on harmful chemical-based pesticides. Consider using non-toxic options such as neem oil, diatomaceous earth, or essential oils to deter pests.
4. Avoid occupational exposure: If you work in an industry that involves handling or working with organophosphates, it is crucial to follow strict safety protocols. Wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and masks, while handling these chemicals. Regularly check your equipment for any leaks or defects, and ensure proper ventilation in the workspace.
5. Promote proper hygiene: Practicing good hygiene habits can significantly reduce the risk of organophosphate poisoning. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and clean water after any potential exposure to pesticides. Avoid touching your face or eating without washing your hands, as residues on the skin or contaminated food can be ingested.
6. Advocate for policy changes: To effectively prevent organophosphate poisoning, it is crucial to advocate for stricter regulations and policies regarding the use and handling of these chemicals. Support local initiatives or organizations that promote safe and sustainable agricultural practices, and encourage your community to adopt these alternatives.
Conclusion: Taking proactive measures to prevent organophosphate poisoning is essential for safeguarding your health and the well-being of your loved ones. By understanding the potential hazards, handling pesticides with caution, exploring alternative methods, avoiding occupational exposure, promoting proper hygiene, and advocating for policy changes, we can collectively work towards minimizing the risk of this serious medical condition. Prioritizing prevention can help ensure a safer and healthier environment for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is organophosphate poisoning?
A: Organophosphate poisoning occurs when a person is exposed to or ingests chemicals known as organophosphates, which are commonly found in pesticides, insecticides, and other agricultural or industrial products. These chemicals can be toxic to the nervous system and can cause a range of symptoms and health problems.
Q: What are the causes of organophosphate poisoning?
A: Organophosphate poisoning can be caused by direct exposure to organophosphate chemicals through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. It can occur in agricultural workers who handle pesticides, as well as in individuals who accidentally ingest or come into contact with these toxic substances.
Q: What are the signs and symptoms of organophosphate poisoning?
A: The signs and symptoms of organophosphate poisoning can vary depending on the level and duration of exposure. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, excessive sweating, abdominal pain, headache, dizziness, muscle weakness, blurred vision, difficulty breathing, and changes in heart rate and blood pressure.
Q: What are the treatment options for organophosphate poisoning?
A: The treatment for organophosphate poisoning involves removing the person from the source of exposure and providing immediate medical care. This may include decontamination of the skin, administration of specific antidotes to counteract the effects of the poison, and supportive measures such as respiratory support, fluid replacement, and medication to control seizures or other symptoms.
Q: How can organophosphate poisoning be prevented?
A: To prevent organophosphate poisoning, it is important to follow safety guidelines when working with pesticides or other chemicals. This includes wearing appropriate protective clothing, using respiratory protection, following proper handling and storage procedures, and ensuring adequate ventilation in work areas. Education and training on the safe use and handling of these chemicals are also crucial in preventing poisoning incidents.
Q: Can organophosphate poisoning be fatal?
A: Yes, organophosphate poisoning can be life-threatening, especially in severe cases or when immediate medical treatment is not provided. It can lead to respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and other complications that may result in death. Prompt recognition and medical intervention are crucial in improving the prognosis of organophosphate poisoning.
Q: Are there long-term effects of organophosphate poisoning?
A: Organophosphate poisoning can have long-term effects on the nervous system, including cognitive impairments, memory problems, mood disorders, and neurobehavioral changes. Chronic exposure to organophosphates has been linked to an increased risk of neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and certain types of cancer. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are recommended for individuals who have experienced organophosphate poisoning.