Paracetamol Overdose
Causes of Paracetamol overdose
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a widely used medication for pain relief and fever reduction. However, when taken in excessive amounts, paracetamol can cause serious complications and even lead to an overdose. Understanding the causes of paracetamol overdose is crucial to prevent such incidents and ensure the safe use of this medication.
There are several factors that can contribute to a paracetamol overdose. One of the main causes is accidental ingestion, especially in young children who might mistake paracetamol for candy or other sweets. It is important to keep medications, including paracetamol, out of reach and in child-resistant containers to avoid such accidents.
Another common cause of paracetamol overdose is intentional self-harm. Unfortunately, paracetamol has become a popular choice for individuals attempting suicide due to its accessibility and perceived safety compared to other medications. This highlights the importance of mental health support and prevention strategies to address underlying issues and reduce the risk of deliberate overdose.
Symptoms and signs of Paracetamol overdose
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a widely used over-the-counter medication for pain relief and fever reduction. However, when taken in excessive amounts, it can lead to a dangerous condition known as Paracetamol overdose. It is essential to recognize the symptoms and signs of Paracetamol overdose to ensure prompt medical intervention and prevent further complications.
One of the initial symptoms of Paracetamol overdose is nausea and vomiting. The excessive intake of Paracetamol can irritate the stomach lining, leading to feelings of nausea and the urge to vomit. Additionally, individuals may experience abdominal pain and tenderness in the upper right side of the abdomen. These symptoms usually occur within the first 24 hours after ingestion.
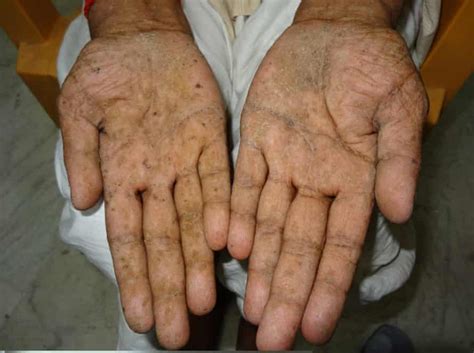
As the Paracetamol overdose progresses, it can cause liver damage. Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, is a prominent sign of liver dysfunction. Individuals may also experience fatigue, weakness, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, Paracetamol overdose can result in liver failure, leading to confusion, bleeding, and even coma.
Treatment options for Paracetamol overdose
Causes of Paracetamol overdose
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a commonly used medication for pain relief and reducing fever. However, taking excessive amounts of paracetamol can be extremely dangerous and may lead to an overdose. It is important to understand the treatment options available in such cases to prevent any further complications.
Symptoms and signs of Paracetamol overdose
Paracetamol overdose can have various symptoms and signs, which can vary depending on the severity of the overdose. Some common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, sweating, and fatigue. If left untreated, serious complications can arise, such as liver damage, kidney failure, and even death.
If you or someone you know experiences a paracetamol overdose, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Prompt treatment can greatly reduce the risk of severe complications. The treatment options for paracetamol overdose generally involve:
- Gastric Decontamination: This method aims to remove as much of the ingested paracetamol as possible from the stomach. It may involve inducing vomiting or administering activated charcoal to absorb the drug.
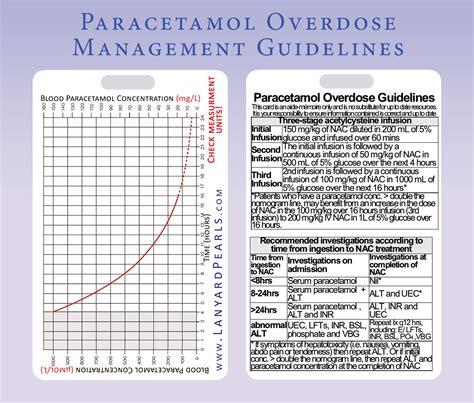
- Acetylcysteine: Acetylcysteine is an antidote commonly used in the treatment of paracetamol overdose. It works by replenishing the levels of glutathione, a natural substance in the body that helps protect the liver from the toxic effects of paracetamol.
- Supportive Care: Depending on the severity of the overdose, supportive care may be necessary. This can include monitoring vital signs, providing fluids intravenously, and addressing any complications that may arise.
Long-term effects of Paracetamol overdose
A paracetamol overdose can have long-term effects on one’s health, especially if not treated promptly. The most significant long-term consequence is potential liver damage. In severe cases, liver failure or the need for a liver transplant may arise. It is vital to understand the importance of early intervention and appropriate treatment to minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Preventing Paracetamol overdose
Preventing paracetamol overdose is crucial for maintaining your health and well-being. Here are some practical steps to help prevent such incidents:
- Read Medication Labels: Always read and follow the instructions and dosage recommendations provided on medication labels.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you have any doubts or questions about paracetamol usage, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
- Keep Medications Secure: Store medications in a safe place, out of reach from children or individuals prone to accidental misuse.
- Do Not Exceed Recommended Dosages: Stick to the recommended dosage and avoid doubling up on doses, especially in a short span of time.
Long-term effects of Paracetamol overdose
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a commonly used medication for pain relief and fever reduction. However, when taken in excessive amounts, it can lead to an overdose and cause serious health complications. In this blog post, we will explore the long-term effects of Paracetamol overdose and discuss the importance of seeking prompt medical attention.
One of the main long-term effects of Paracetamol overdose is liver damage. The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing drugs, including Paracetamol. When an overdose occurs, the liver may become overwhelmed and unable to effectively process the excess medication. This can result in liver toxicity, which can range from mild inflammation to severe liver failure. It is essential to understand that liver damage from Paracetamol overdose may not manifest immediately and can take several days to become apparent.
Another potential long-term effect of Paracetamol overdose is kidney damage. Similar to the liver, the kidneys also help eliminate waste products from the body, including drugs. High doses of Paracetamol can lead to kidney injury, especially if the overdose is not promptly treated. Symptoms of kidney damage may include decreased urine output, swelling in the legs and ankles, and fatigue. In severe cases, acute kidney failure may occur, requiring dialysis or even kidney transplantation.
Preventing Paracetamol overdose
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a common pain reliever and fever reducer that is widely available over the counter. While it is generally safe when used as directed, it can be dangerous if taken in excessive amounts. Preventing Paracetamol overdose is crucial to ensure the wellbeing of individuals. There are several steps that can be taken to minimize the risk of accidental or intentional overdose.
1. Read and Follow the Dosage Instructions: One of the most important steps in preventing Paracetamol overdose is to carefully read and follow the dosage instructions provided on the packaging or as directed by a healthcare professional. It is essential to avoid exceeding the recommended dose, as higher doses can put unnecessary stress on the liver.
2. Use Only One Paracetamol-Containing Product at a Time: Many medications, both prescription and over the counter, contain Paracetamol as an active ingredient. It is crucial to be aware of the products you are taking and avoid using multiple medications that contain Paracetamol simultaneously. Combining these medications can increase the risk of exceeding the safe dosage limit.
3. Be Cautious with Combination Products: Some medications, such as cold and flu remedies, may contain a combination of ingredients, including Paracetamol. Carefully read the labels of these products to determine the amount of Paracetamol they contain. Using multiple combination products together can lead to unintentional overdose.
- 4. Store Medications Safely: Ensure that Paracetamol and other medications are stored out of the reach of children and pets. Keep them in a secure location, such as a locked cabinet, to prevent accidental ingestion.
- 5. Seek Professional Advice: If you are unsure about the safe use of Paracetamol or have concerns about potential drug interactions, consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance based on your individual needs and medical history.
| Risk Factors for Paracetamol Overdose: |
|---|
| ➢ Previous history of overdose |
| ➢ Chronic alcohol use |
| ➢ Liver disease |
| ➢ Concurrent use of certain medications |
| ➢ Psychological factors |
By taking these preventive measures, the risk of Paracetamol overdose can be significantly reduced. It is crucial to be mindful of the dosage, avoid concurrent use of Paracetamol-containing products, and seek professional advice when in doubt. By prioritizing safety and responsible medication usage, individuals can ensure a healthier and safer approach to pain relief.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What are the causes of Paracetamol overdose?
Paracetamol overdose can occur due to intentional or accidental ingestion of a large quantity of the medication. It can also happen when individuals exceed the recommended dose, or when they combine multiple medications containing Paracetamol without realizing it.
Question 2: What are the symptoms and signs of Paracetamol overdose?
The symptoms and signs of Paracetamol overdose may initially be mild, such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. However, as the overdose progresses, it can lead to more severe symptoms like yellowing of the skin or eyes, excessive sweating, confusion, and even liver damage.
Question 3: What are the treatment options for Paracetamol overdose?
The treatment for Paracetamol overdose typically involves administering a medication called N-acetylcysteine (NAC) to prevent liver damage. NAC is most effective when given within 8-10 hours after the overdose, but it can still provide some benefit even if started later.
Question 4: What are the long-term effects of Paracetamol overdose?
Paracetamol overdose can cause serious long-term effects, particularly if liver damage occurs. In severe cases, it can lead to liver failure, which may require a liver transplant. Additionally, repeated or chronic overdoses can result in chronic liver disease or other complications.
Question 5: How can Paracetamol overdose be prevented?
To prevent Paracetamol overdose, it is important to always follow the recommended dose and dosage frequency provided by healthcare professionals or as stated on the packaging. Individuals should also be cautious about combining Paracetamol with other medications and should consult a healthcare professional before doing so.
Question 6: Can Paracetamol overdose be fatal?
Yes, Paracetamol overdose can be fatal, particularly if it leads to severe liver damage. Prompt medical intervention is crucial in preventing the life-threatening complications associated with Paracetamol overdose.
Question 7: What should I do if I suspect a Paracetamol overdose?
If you suspect a Paracetamol overdose, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention or contact your local poison control center. Do not wait for symptoms to worsen, as early treatment can significantly improve the outcome and reduce the risk of long-term complications.