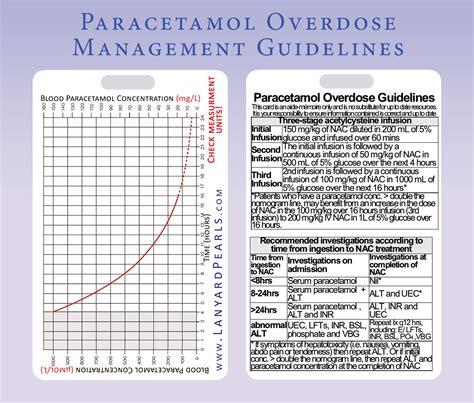
Antifreeze Poisoning
What is Antifreeze Poisoning?
Antifreeze poisoning is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when an individual ingests or comes into contact with antifreeze, which is a liquid used to prevent freezing in vehicles and other machinery. Antifreeze contains a toxic substance called ethylene glycol, which is highly poisonous to humans and animals.
There are several common sources of antifreeze poisoning. The most common source is accidental ingestion, usually by children or pets. Antifreeze has a sweet taste that may be enticing to animals and young children, leading them to consume it unknowingly. Another source of poisoning is inhalation of antifreeze fumes, which can occur in poorly ventilated areas or during the disposal of used antifreeze. Additionally, skin contact with antifreeze may also result in poisoning.
If someone has been exposed to antifreeze, it is important to be aware of the symptoms and signs of poisoning. The initial symptoms may be similar to alcohol intoxication, including dizziness, confusion, and lack of coordination. As the poisoning progresses, more severe symptoms may develop, such as rapid breathing, increased heart rate, kidney damage, and even coma. Recognizing these signs early on is crucial for prompt medical intervention.
- Immediate steps to take if suspected antifreeze poisoning:
- Call emergency services or a poison control center to seek immediate medical assistance.
- Do not induce vomiting unless instructed to do so by a healthcare professional.
- If skin contact has occurred, remove contaminated clothing and rinse the affected area with water.
- Provide as much information as possible about the exposure, including the type and amount of antifreeze ingested or contacted.
Preventing antifreeze poisoning is essential to ensure the safety of both humans and animals. Some preventive measures include storing antifreeze in properly labeled containers and in a secure location out of reach of children and pets. It is also important to clean up any spills immediately and dispose of used antifreeze properly. Additionally, consider using antifreeze products that contain propylene glycol instead of ethylene glycol, as they are less toxic.
In conclusion, antifreeze poisoning is a serious health concern that can result from ingesting or coming into contact with antifreeze. Understanding the sources, symptoms, and immediate steps to take in case of suspected poisoning is crucial. By implementing preventive measures, such as proper storage and disposal, we can help reduce the risk of antifreeze poisoning and protect the well-being of both humans and animals.
Common Sources of Antifreeze Poisoning
Antifreeze poisoning is a serious and potentially fatal condition that occurs when an individual ingests or inhales antifreeze. It is important to be aware of the common sources of antifreeze poisoning in order to prevent accidental exposure and protect the well-being of both humans and animals.
One of the most common sources of antifreeze poisoning is automotive antifreeze. This is typically a bright-colored liquid that is used in vehicle cooling systems to prevent freezing and overheating. The main ingredient in automotive antifreeze is ethylene glycol, which is highly toxic when ingested. It is important to store automotive antifreeze in a secure location and dispose of it properly to prevent accidental ingestion by curious children or pets.
Another potential source of antifreeze poisoning is household products that contain antifreeze. For example, some windshield washer fluids, radiator cleaners, and brake fluids may contain ethylene glycol. These products are commonly stored in garages or workshops, making them easily accessible to both children and pets. It is crucial to store these products in a locked cabinet or out of reach to prevent accidental ingestion.
Lastly, improper disposal of antifreeze can contribute to environmental contamination and pose a risk to wildlife. When antifreeze is poured onto the ground or into storm drains, it may end up in bodies of water where animals may consume it unknowingly. Ensuring that antifreeze is disposed of safely and responsibly is essential to prevent poisoning incidents and protect the environment.
- In conclusion, being aware of the common sources of antifreeze poisoning is crucial for prevention. Automotive antifreeze, household products, and improper disposal can all contribute to accidental exposure to ethylene glycol. By taking steps to properly store and dispose of antifreeze products, we can help ensure the safety of both humans and wildlife.
| Common Sources of Antifreeze Poisoning: |
|---|
| Automotive antifreeze |
| Household products containing antifreeze |
| Improper disposal of antifreeze |
Symptoms and Signs of Antifreeze Poisoning
Antifreeze poisoning is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when an individual ingests or inhales antifreeze liquids or fumes. It is important to be aware of the symptoms and signs of antifreeze poisoning in order to identify and seek appropriate medical attention as soon as possible. Antifreeze, also known as coolant, is a toxic substance that is commonly used in vehicles to prevent the freezing of engines. However, it contains chemicals such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, which can be extremely harmful if ingested.
There are several symptoms and signs that may indicate antifreeze poisoning. It is crucial to recognize these signs and take immediate action, as delayed treatment can lead to serious complications and even death. Some of the common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. These gastrointestinal symptoms may begin within the first few hours of ingestion and can quickly progress to more severe effects.
In addition to gastrointestinal symptoms, antifreeze poisoning can also cause central nervous system effects. Individuals may experience dizziness, confusion, slurred speech, and difficulty walking. These neurological symptoms can indicate significant damage to the brain and require immediate medical attention. Other signs of antifreeze poisoning include rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, and seizures.
If you or someone you know exhibits any of these symptoms after potential exposure to antifreeze, it is crucial to take immediate steps to prevent further harm. First and foremost, contact emergency medical services or poison control helpline for guidance. Time is of the essence in antifreeze poisoning cases, and early medical intervention can greatly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
While waiting for medical assistance, it is important to prevent further ingestion of antifreeze. Keep the individual calm and ensure they do not consume anything else. If there are any visible signs of antifreeze on the skin, rinse it off immediately with plenty of water. However, do not induce vomiting or administer any home remedies without professional guidance.
In summary, recognizing the symptoms and signs of antifreeze poisoning is crucial to ensure prompt medical attention. Symptoms such as gastrointestinal distress, neurological effects, and cardiovascular abnormalities should never be ignored. Immediate steps should be taken to prevent further ingestion and seek professional help. By being aware of the signs and acting swiftly, the chances of a positive outcome can be significantly increased in cases of antifreeze poisoning.
Immediate Steps to Take if Suspected Antifreeze Poisoning
Immediate Steps to Take if Suspected Antifreeze Poisoning
If you suspect that someone, including a pet, has been exposed to antifreeze and may be experiencing antifreeze poisoning, it is essential to take immediate action as this can be a life-threatening situation. Antifreeze poisoning occurs when a person or animal ingests ethylene glycol, which is the main ingredient in most antifreeze products. This toxic substance can cause severe damage to the kidneys and other vital organs if not treated promptly. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of antifreeze poisoning and taking the right steps can make a significant difference in preventing further harm.
When it comes to antifreeze poisoning, time is of the essence. If you notice someone exhibiting symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion, or seizures, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Call emergency services or take the individual to the nearest emergency room as soon as possible. Prompt medical evaluation is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment.
While waiting for medical help, there are a few steps you can take to help mitigate the effects of antifreeze poisoning. Do not induce vomiting unless directed to do so by a healthcare professional as it can potentially worsen the situation. If the exposure was recent (within the last 30 minutes), rinsing the mouth with water can help dilute the toxic substance. However, do not force the individual to drink water or any other fluid.
Additionally, if you suspect antifreeze poisoning in a pet, it is vital to contact a veterinarian immediately. They will provide guidance on the next steps, which may include inducing vomiting or bringing the pet to the clinic for treatment. Never attempt to treat antifreeze poisoning in pets at home, as they require specialized care.
In conclusion, suspected antifreeze poisoning is a serious matter that requires swift action. The key is to seek medical help without delay and follow the instructions of healthcare professionals. Remember, prevention is always the best approach, so make sure to take necessary precautions to avoid exposure to antifreeze. Stay vigilant, keep antifreeze products securely stored, and be cautious when handling and disposing of them, especially if you have pets or young children around.
Preventing Antifreeze Poisoning
The prevention of antifreeze poisoning is crucial in ensuring the safety of both humans and animals. Antifreeze, also known as engine coolant, is a liquid used to regulate the temperature of engines. However, it contains a highly toxic substance called ethylene glycol, which can be lethal if ingested. In order to prevent antifreeze poisoning, it is important to be aware of the potential sources, understand the symptoms, and take the necessary steps to keep it out of reach.
There are several common sources of antifreeze poisoning that people should be mindful of. One of the most common sources is leaking car radiators. If a car radiator is leaking, the antifreeze can end up on the ground, posing a danger to pets and wildlife. Spilled or improperly stored antifreeze containers can also be a source of poisoning. It is important to always store antifreeze in sealed containers and clean up any spills immediately. Additionally, antifreeze can sometimes be found in other products such as windshield washer fluid, so it is essential to read labels carefully and ensure that any potentially toxic substances are stored securely.
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of antifreeze poisoning is crucial in order to provide immediate medical attention. Symptoms can vary depending on the amount ingested and may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, seizures, and even coma. Increased thirst and frequent urination may also be observed. If you suspect antifreeze poisoning, it is vital to seek veterinary or medical help right away, as early treatment can greatly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
- Be mindful of car radiator leaks and clean them up promptly.
- Store antifreeze in sealed containers and clean up any spills immediately.
- Read labels carefully and securely store any products that contain antifreeze.
- Keep antifreeze out of reach of children and pets.
- Dispose of antifreeze properly at designated collection sites.
Preventing antifreeze poisoning is crucial for the safety of our loved ones, both human and animal. By being vigilant about potential sources, understanding the symptoms, and taking proactive steps to secure and dispose of antifreeze, we can greatly reduce the risk of poisoning incidents. Remember, a little prevention can go a long way in keeping our homes and environment safe.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What is Antifreeze Poisoning?
Antifreeze poisoning occurs when a person or animal ingests or inhales antifreeze, which contains a toxic chemical called ethylene glycol. It can be extremely dangerous and even deadly if left untreated.
Question 2: What are the common sources of Antifreeze Poisoning?
The most common source of antifreeze poisoning is accidental ingestion of automotive antifreeze, which is often sweet-tasting and appealing to animals and children. Other potential sources include leaking car radiators, improperly stored antifreeze containers, and industrial products containing ethylene glycol.
Question 3: What are the symptoms and signs of Antifreeze Poisoning?
The symptoms of antifreeze poisoning may vary depending on the amount ingested and the individual’s body weight. Common signs include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, increased thirst, excessive urination, rapid breathing, confusion, seizures, and eventual kidney failure.
Question 4: What immediate steps should be taken if suspected Antifreeze Poisoning?
If antifreeze poisoning is suspected, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Contact a poison control center or emergency medical services for proper guidance. Do not induce vomiting unless directed by medical professionals.
Question 5: How can Antifreeze Poisoning be prevented?
To prevent antifreeze poisoning, it is important to store antifreeze in sealed containers and in a secure location out of reach of children and animals. Additionally, addressing any leaks in car radiators promptly and properly disposing of used antifreeze can help reduce the risk.
Question 6: Are there any safer alternatives to traditional antifreeze?
Yes, there are alternative antifreeze products available that use propylene glycol instead of ethylene glycol. Propylene glycol is less toxic and poses a lower risk to humans and animals if accidentally ingested. It is important to always read product labels and consult professionals for safe handling and usage.
Question 7: Is it possible to treat Antifreeze Poisoning?
Yes, if treated promptly, antifreeze poisoning can be treated. The primary treatment is the administration of an antidote called fomepizole or ethanol, which can prevent the toxic effects of ethylene glycol. However, it is essential to receive medical treatment as soon as possible for the best chance of recovery.